ARL’s (Army Research Laboratory) Frank Gardea, a research engineer, said the focus of the research was on controlling how molecules interact with each other. He said the aim was to “have them interact in such a way that changes at a small size, or nanoscale, could lead to observed changes at a larger size, or macroscale”. “An important motivation for this work is the desire to engineer new structures, starting from the nanoscale, to enable advanced rotorcraft concepts that have been proposed in the past but were infeasible due to limitations in current composites,” said Bryan Glaz, chief scientist of ARL’s Vehicle Technology Directorate.
One of the most important capabilities envisioned by these concepts is a significantly reduced maintenance burden due to compromises we make to fly at high speeds.The reduced scheduled maintenance of future Army aviation platforms is an important technological driver for future operating concepts. The enhanced mechanical properties with potentially low weight penalties enabled by the new technique could lead to nanocomposite-based structures that would enable rotorcraft concepts that we cannot build today.
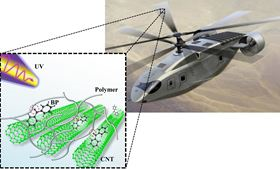
The joint work shows that these composite materials can become 93% stiffer and 35% stronger after a five-minute exposure to UV light. The technique consists of attaching UV light-reactive molecules to reinforcing agents like carbon nanotubes, which are then embedded in a polymer. Exposure to UV light triggers a chemical reaction that enhances the interaction between the reinforcing agents and the polymer, making the material stiffer and stronger.
The researchers said the chemistry used in this technique is generally applicable to a variety of reinforcement/polymer combinations, thereby expanding the utility of this control method to a wide range of material systems. “This research shows that it is possible to control the overall material property of these nanocomposites through molecular engineering at the interface between the composite components. This is not only important for fundamental science but also for the optimization of structural component response,” said Zhongjie Huang, a postdoctoral research fellow at the University of Maryland.
Future structures based on this work may help lead to new composites with controlled structural damping and low weight that could allow the development of low maintenance, high speed rotorcraft concepts that are currently not feasible (e.g. soft in-plane tiltrotors). In addition, controllable mechanical response will allow for the development of adaptive aerospace structures that could potentially accommodate mechanical loading conditions.
Collaboration between the ARL and the (UMD) was crucial for the development of this technique. “In our lab at UMD we have been developing unique carbon nanomaterials and chemistry, but it was not until Gardea approached us did we become aware of the intriguing challenge and opportunity for reconfigurable composite materials,” said YuHuang Wang, professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of Maryland. “Together we have achieved something that is quite remarkable.”