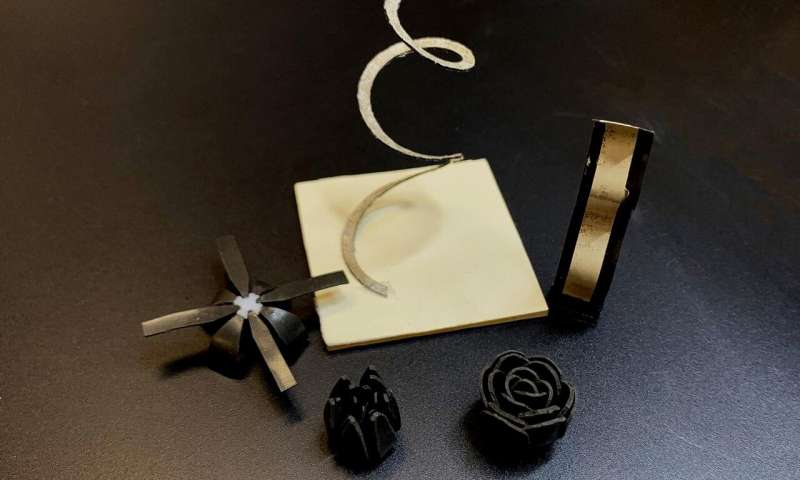
A team of researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology and The Ohio State University has developed a soft polymer material, called magnetic shape memory polymer, that uses magnetic fields to transform into a variety of shapes. The material could enable a range of new applications from antennas that change frequencies on the fly to gripper arms for delicate or heavy objects.
The material
The material is a mixture of three different components, all with unique characteristics: two types of magnetic particles, one for inductive heat and one with strong magnetic attraction, and shape-memory polymers to help lock various shape changes into place. “This is the first material that combines the strengths of all of these individual components into a single system capable of rapid and reprogrammable shape changes that are lockable and reversible,” said Jerry Qi, a professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering at Georgia Tech. The research, which was reported Dec. 9 in the journal «Advanced Materials».
The process
To make the material, the researchers began by distributing particles of neodymium iron boron (NdFeB) and iron oxide into a mixture of shape memory polymers. Once the particles were fully incorporated, the researchers then moulded that mixture into various objects designed to evaluate how the material performed in a series of applications. For example, the team made a gripper claw from a t-shaped mould of the magnetic shape memory polymer mixture. Applying a high-frequency, oscillating magnetic field to the object caused the iron oxide particles to heat up through induction and warm the entire gripper. That temperature rise, in turn, caused the shape memory polymer matrix to soften and become pliable. A second magnetic field was then applied to the gripper, causing its claws to open and close. Once the shape memory polymers cool back down, they remain locked in that position.
Possible applications
The shape-changing process takes only a few seconds from start to finish, and the strength of the material at its locked state allowed the gripper to lift objects up to 1,000 times its own weight. “We envision this material being useful for situations where a robotic arm would need to lift a very delicate object without damaging it, such as in the food industry or for chemical or biomedical applications,” Qi said. The new material builds on earlier research that outlined actuation mechanisms for soft robotics and active materials and evaluated the limitations in current technologies. “The degree of freedom is limited in conventional robotics” said Ruike (Renee) Zhao, an assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at Ohio State. “With soft materials, that degree of freedom is unlimited.” The researchers also tested other applications, where coil-shaped objects made from the new material expanded and retracted – simulating how an antenna could potentially change frequencies when actuated by the magnetic fields. “This process requires us to use of magnetic fields only during the actuation phase,” Zhao said. “So, once an object has reached its new shape, it can be locked there without constantly consuming energy.”
This research was supported by The Ohio State University Materials Research Seed Grant Program, funded by the National Science Foundation’s Center for Emergent Materials under grant No. DMR-1420451. The project was also supported by the Center for Exploration of Novel Complex Materials, the Institute for Materials Research, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under grant No. FA9550-19-1-0151, the U.S. Department of Energy under grant No. DE-SC0001304, and by grants from the Haythornthwaite Foundation. The content is the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the sponsoring agencies.
CITATION: Qiji Ze, Xiao Kuang, Shuai Wu, Janet Wong, S. Macrae Montgomery, Rundong Zhang, Joshua M. Kovitz, Fengyuan Yang, H. Jerry Qi, and Ruike Zhao, “Magnetic Shape Memory Polymers with Integrated Multifunctional Shape Manipulations” (Advanced Materials, 2019) : http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adma.201906657
Source: Georgia Tech