In the publicly funded cooperation project “Automated Repair Patch Production – ARP2”, the Institut für Textiltechnik (ITA) in Aachen, is developing a process chain for the automated production of repair patches for Fiber-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) components in cooperation with the Sabanci University (Istanbul).
Aim of repair is to restore the mechanical properties of a damaged component. Thereby the aspects power flow, reliability and economy are in part clearly contradictory. Various repair strategies have been established in the past. However, the basic repair procedure remains the same. Thus, each repair process starts with the damage detection. It is examined whether the damaged component can be repaired or whether a replacement is necessary, this often depends on the construction (integral or differential design method). If a repair takes place, the repair method is selected and carried out in the next step. However, the industrially established repair process is characterized by a high amount of manual work in all process steps.
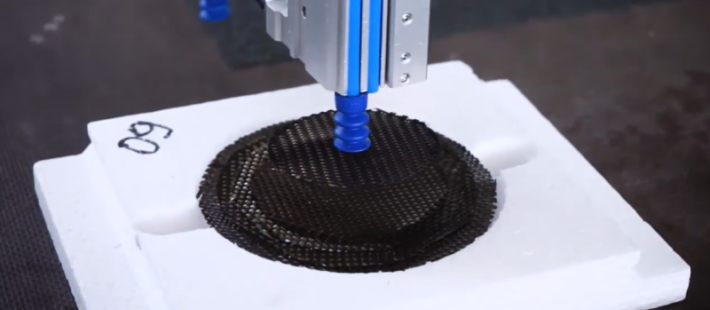
The available results of the ARP2 project prove that it is possible to partially automate the repair process of FRP components on a demonstrator geometry. The placement of the repair patch is still done manually even with the newly developed repair process. The precision in stacking the individual textile layers is defined by the industrial robot used and the process dynamics. The developed packaging enables the transport of flat repair patches and protects them from enviroment and mechanical influences.
The project is funded by the BMBF and DLR and it develops in partnership with Sabanci University, Turkey.
Featured image: A process chain for the automated production of repair patches for FRP components – Source: ITA
Source: Institut für Textiltechnik