The ThermoPlastics composites Research Center (TPRC, Enschede, Netherlands), is currently investigating a two-step approach for the manufacturing of thermoplastic composite structures, involving the rapid deposition of preimpregnated thermoplastic tape, using automated fiber placement (AFP) followed by vacuum-bag-only (VBO) consolidation. Compared to the AFP with in-situ consolidation alternative, TPRC says its AFP + VBO project combines the lay-down of tape material at a cost-effective rate and an affordable post-processing step to ensure the required consolidation quality.
Project aim
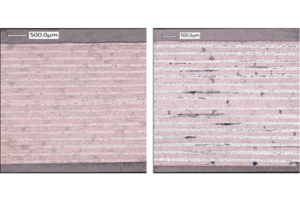
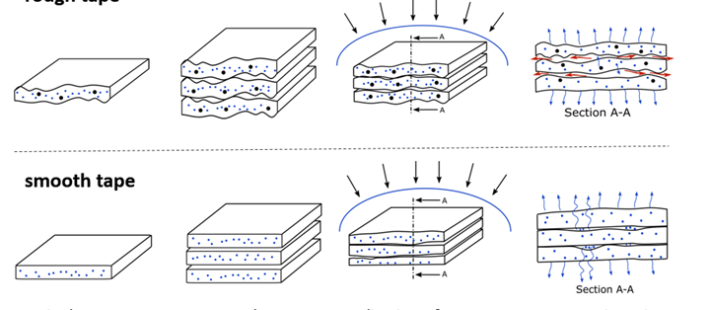
The main aim of the project, TPRC says, is to enable the cost-efficient out-of-autoclave (OOA) manufacture of advanced components by developing material guidelines and process models. This requires a thorough understanding of the physical mechanisms that control the OOA consolidation of fiber-placed thermoplastic laminates — for example, the in-plane permeation and diffusion of entrapped air during different stages of the consolidation process for various material configurations (Figure 1). TPRC says the mechanisms have been explored qualitatively, as seen through the effect of sealing the edges of a stack on air removal (Figure 2).
The research center notes that the research is still ongoing, and measurement set-ups are being developed for the quantitative determination of both diffusion and permeation related material properties.
Figure 1 (Featured image). Different air removal mechanisms such as in-plane permeation and through-thickness diffusion for, respectively, rough tape (top) and smooth tape (bottom). Source | TPRC
Source: TPRC