Recently, the results of the H2REF project, including the main findings, have been presented. The project aimed to develop an advanced new compression and buffering solution for hydrogen refuelling stations (HRS) of 70 MPa passenger FC-vehicles. This solution is based on the use of hydro-pneumatic accumulators, which provides a more reliable and economical solution while improving performance. The project was developed by a consortium of six partners from European countries (France, Germany, Norway and United Kingdom) bringing together the key experience, knowledge base and resources for reaching the objectives of the project.
How the consortium is structured
The project is structured around distinct work plans, developed around technical work packages specifically tailored to the strengths of each consortium member illustrating both the comprehensiveness of the consortium’s capabilities as well as the complementarity of the partnership. The focus from the two main industrial partners Haskel and Hexagon is in the continued development of this compression technology, with the view of eventually jointly developing a highly competitive Compression and Buffering Module (CBM) product offer. This aim certainly has the potential of a major commercial breakthrough if the project results are achieved. H2Nova, as developer and owner of intellectual property and CCS with expertise in RCS development and compliance are also interested in such a development. Cetim and LBST will support the consortium with their wealth of knowledge of experience in this particular field of development.
The basic concept
Bladder accumulator-based compression is applicable to any refuelling applications, thanks to the combined high scalability of hydraulics technology and carbon composite pressure vessels. Indeed, high pressure hydraulic pumps are already available and successfully delivering very large capacities for many oil and gas applications. Similarly, high pressure accumulators in carbon composite material are also currently available and can be built to very large sizes.
Main advantage of the concept compared to conventional technologies
A fundamental advantage of bladder accumulator-based compression for compression and transfer of hydrogen over conventional mechanical compression, is that it uses serially produced components from a mature and standardized industry (hydraulics and composite pressure vessels) with a world-wide supplier base, minimising cost while providing excellent robustness and reliability.

Other advantages of the concept compared to conventional technologies
Furthermore, bladder accumulator-based compression provides the following additional benefits:
- high scalability, thanks to the combined high scalability of hydraulics and carbon composite pressure vessels;
- high flexibility, thanks to the wide operating pressure ranges of the components;

- high flow-rate and small foot-print: as compression effort is applied by means of a working fluid driven by a hydraulic pump;
- maximized compression capacity, thanks to uniquely taking advantage of varying pressure upstream, while operating at constant power (even though the discharge pressure to suction pressure ratio changes);
- reduced energy consumption, thanks to the exploitation of upstream pressure:
- the average energy consumption is halved as the pressure of the stored hydrogen is fully taken advantage of;
- the on-going adoption of higher storage pressure in the hydrogen supply chain further increases the benefit of taking fully advantage of the source storage pressure;
- improved reliability and reduced maintenance requirements, intrinsic to hydraulic power technology;
- exploitation of the full compression power capacity at all times, maximizing effective throughput.
What does it do?
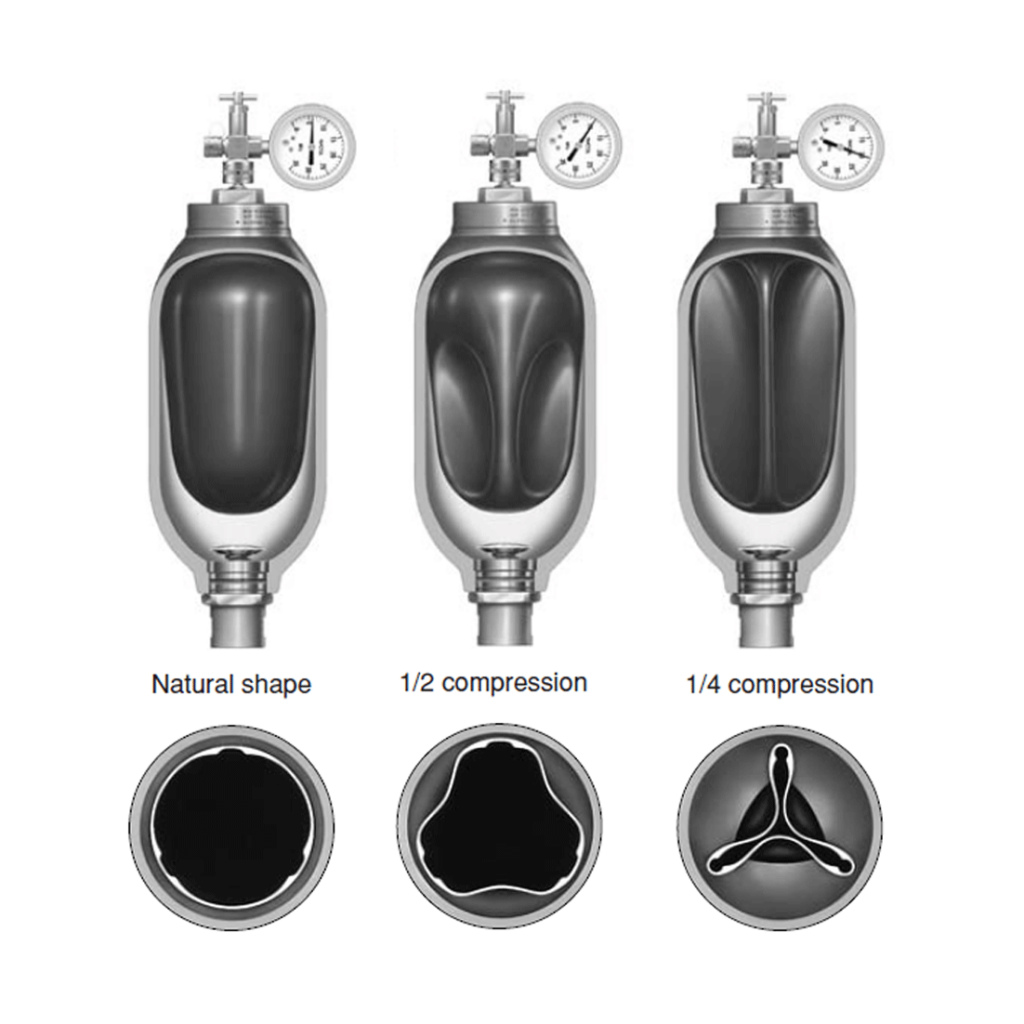
The H2REF concept is based on the use of high-pressure hydro-pneumatic bladder accumulators in carbon composite material, for performing compression as well as buffering if needed. Bladder accumulators, where fluid compression and/or displacement can be achieved by changing the internal volume of a bladder in elastomer material, thanks to the application of hydraulic pressure, as shown below, are the most common type of hydro-pneumatic accumulator and are used in a very wide variety of applications and operating conditions with a diversity of fluids.
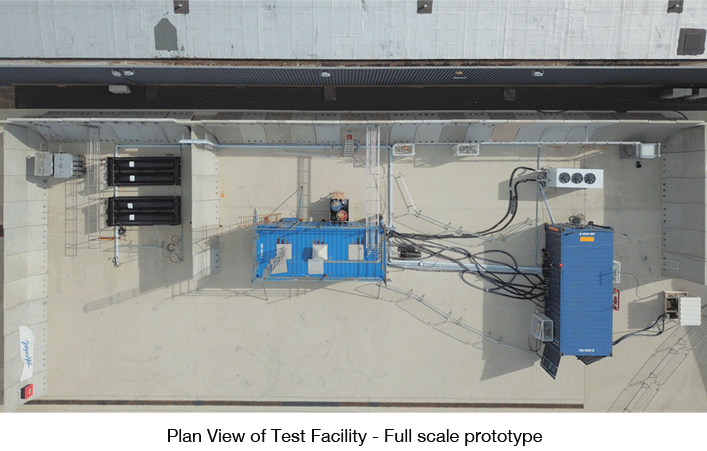

Results
First of a kind high-pressure bladder accumulators in composite material, for operation at up to 90 MPa with demonstrated lifetime.
H2REF has received funding from the Fuel Cells and Hydrogen 2 Joint Undertaking under grant agreement No 671463. This Joint Undertaking receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and Hydrogen Europe and Hydrogen Europe Research.
Source: H2REF – The text is modified with editorial changes by Compositi magazine.
Images – Credit: H2REF