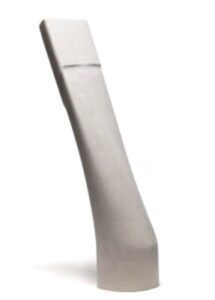
As the demand for composite parts increases, so does the need for more efficient and cost-effective production solutions. Massivit recently launched the 10000 machines, and its additively produced mandrels are ideal for forming hollow composite parts with smooth interior surfaces. We will discuss the advantages of printing with water breakable material, as well as the cost savings that can be realised.
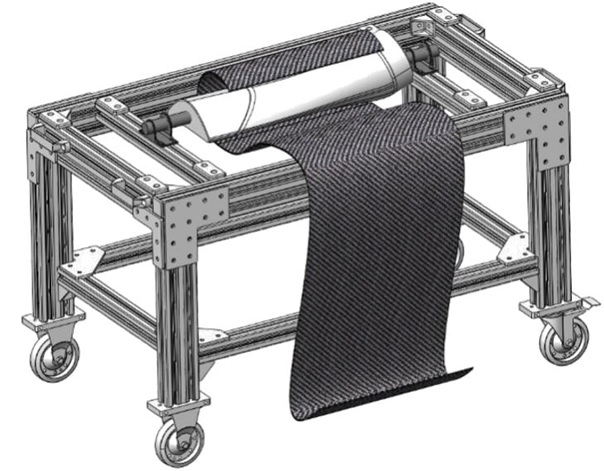
Mandrels & Composite Parts
Mandrels are typically cylindrical tools or devices around which a workpiece can be shaped and find usefulness in the manufacture of composites parts where they act as sacrificial tools around which composite material is placed and cured before the mandrels are removed. They are used in the manufacture of tubular components and parts such as general pipes, bike frames, exhaust pipes and construction air ducts.
There are many ways to make mandrels, but the most common method is to start with a piece of round stock that has been cut to the desired length. This stock is then put into a lathe and machined to the desired shape. In some cases, multiple pieces of stock may be welded together to create a larger mandrel, which once machined to the correct shape, may be heat-treated to improve strength and durability.
Traditional methods of making mandrels are relatively problematic as they require a lot of time and effort to make. The process is often complicated, and it can be difficult to get the mandrels to the right precise size and shape. Conventional methods also often involve the use of a significant amount of manual labor, which can be time-consuming and result in inconsistency between different mandrels.
Advantages of 3D Printing
Massivit — a leading provider of large-format 3D printing solutions — has developed a proprietary printing process for producing lightweight, yet strong and durable mandrels. This represents a highly innovative solution to produce composite parts, offering significant advantages over traditional manufacturing methods and enabling the production of high-quality composite parts with reduced lead times and lower costs.
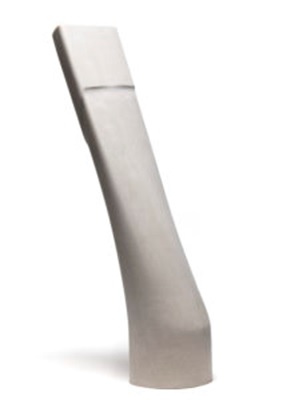

One of the key advantages of using 3D printing or Additive Manufacturing (AM) to make mandrels is that it allows for much more complex designs than traditional machining methods. With AM, there are no constraints on the geometric shapes that can be produced, meaning that mandrels can be made with very intricate designs. Additionally, AM can be used to produce mandrels made from materials that are difficult or impossible to machine using traditional methods. This opens a whole new range of possibilities for mandrel designs and means that they can be tailor-made to suit the specific needs of a particular application.
Also, whereas traditional mandrel manufacture may require multiple parts to be assembled to make the final mandrel shape, Additive Manufacturing allows production of a single monolithic mandrel saving time and money.
The Massivit 10000
Mandrels can be digitally produced on the Massivit 10000 AM system. The Massivit 10000 is an industrial-grade 3D printer for fast and efficient production of mandrels, large tools, and molds. The machine uses proprietary Cast In Motion (CIM) technology in combination with Massivit’s patented Gel Dispensing Printing (GDP) method, which allows direct casting of the mold into a 3D printed sacrificial shell.
To achieve this, the Massivit 10000 utilizes a dual-head system, ultra-fast patented technology, and for the mandrels uses water-breakable material that deconstructs in water. All these allow manufacturers to produce complex mandrels within a matter of days instead of weeks.
Water Breakable Material
At the heart of the AM mandrel building process from Massivit is the water-breakable material, perfectly suited to the production of mandrels. Obviously, one of the most notable features of the material is that it is water breakable, crumbling in water without dissolving leaving the water uncontaminated and ready for reuse. This allows the mandrel to be easily removed from the final product after production, so the demolding process is quick as well.
The material is also lightweight (making it easy to handle and transport during the production process); strong and durable (allowing it to be used for a variety of mandrel applications); easy to use, (so it can be easily molded into the desired shape and size for the mandrel); environmentally friendly, (as it does not release any harmful chemicals or pollutants into the environment); and speedy, with mandrels printing in a matter of hours.
Additionally, providing high quality interior surfaces of these hollow complex components is not a problem at all. An exceptionally smooth internal surface for parts like air ducts can be achieved
A Real Revolution
Mandrels made using AM and more specifically via the Massivit 10000 have the potential to revolutionize the way composite parts and components are made. Mandrels produced using AM offer several advantages over traditionally manufactured mandrels. They are lighter, more precise, and can be easily customized to fit the specific needs of each part. This results in faster production times and a reduction in waste. In addition, mandrels made using AM can be produced from advanced materials that are stronger, more durable, and able to withstand higher temperatures, and as we have seen water breakable simplifying removal.
This enables the production of composite parts that are of higher quality, more reliable and have a longer lifespan. The future of composite part manufacturing is bright with the advent of additively manufactured mandrels, and this technology is poised to revolutionize the industry.