The Institut für Textiltechnik (ITA) of RWTH Aachen University demonstrates its expertise along the entire process chain at the joint stand of the Aachen Center for Integrative Lightweight Production (AZL) of RWTH Aachen University in Hall 6 booth No. C79. ITA shows its knowledge from the raw material over the fibre up to innovative textiles and whole components. Exclusive innovative processes and products will be presented with different demonstrators. The exhibits come from different application fields: From aerospace and automotive applications to construction and housing and also medical uses.
Laser processing
The ITA presents the enormous potential of laser material processing for the production of composite components and the implementation of fasteners for multi-material design applications in an exhibit which is a world novelty. Fasteners which were so far pasted into or glued on now can be custom-fit integrated in textile preforms by using ultra-short pulsed laser radiation. Complex drilling, surface preparation or curing process of the adhesives is no longer required. The pull-out forces are increased significantly and the process times are reduced by the new process. These advantages are mainly of interest to the automotive and aerospace industry.
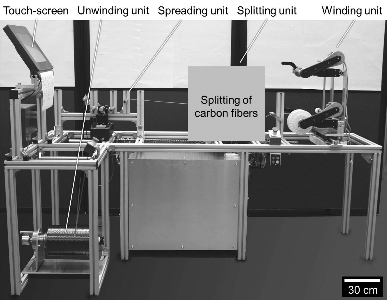
SSM Carbon
The new machine SSM carbon features a modular design and spreads, splits and winds carbon fibres. As a first step, we spread cost-effective heavy tows made of carbon fibres with 50 K single filaments which are divided into split tows with a defined number of filaments between 3 K and 12 K. This procedure reduces the costs significantly for light tows. Additionally, a tailor-made number of single filaments can be produced. The ITA is responsible for labscale tests and concept development for a scale-up of the machine technology and the expansion of the plant in close cooperation with the partner companies.
Innovative 3D tufting unit
The joining of textile preforms represents a central process in the production of components made of fibre-reinforced composites. The tufting technologies which are currently commercially available have too low sewing speeds. A new tufting unit with a sewing speed of up to 1,000 stitches per minute was developed and the tufting head which was developed in the project “3D Tuft” will be presented at JEC 2017.
Car roof segment
The car roof segment was completely produced for the first time out of integral reinforced fabrics. The textile architecture according to load paths allows the reduction of component weight by a higher exploitation of the fibre properties. Production costs will decrease through less waste and process steps during preforming because the single integral reinforced layers are manufactured in a single step by open reed weaving.
Textile-reinforced concrete table
The table made out of textile-reinforced concrete (TRC) visualises the enormous future potential of this innovative composite material. This potential is based on the high load bearing capacity of textile-reinforced concrete components as well as their resistance to corrosion compared to conventional reinforced concrete. The flexible textile reinforcement allows the production of thin, individually shaped and light concrete structures, which offer outstanding mechanical characteristics and durability. The conception for this textile-reinforced concrete table is based on a quadraxial carbon fibre fabric, which is coated with epoxy resin. As a result the tabletop has almost isotropic properties which allow a thickness of only 15 mm. The potential target groups are manufacturing companies specialised on textile- or concrete products as well as construction companies.