The University of Surrey has developed a robust multi-layed nano-barrier for ultra-lightweight and stable carbon fibre reinforced polymers (CFRPs) that could be used to build high precision instrument structures for future space missions.
CFRP is used in current space missions, but its applications are limited because the material absorbs moisture. This is often released as gas during a mission, causing the material to expand and affect the stability and integrity of the structure. Engineers try to minimise this problem with CFRP by performing long, expensive procedures such as drying, recalibrations and bake-out- all of which may not completely resolve the issue.
In a paper published by the journal «Nature Materials», scientists and engineers from Surrey and Airbus Defence and Space detail how they have developed a multi-layered nano-barrier that bonds with the CFRP and eliminates the need for multiple bake-out stages and the controlled storage required in its unprotected state.
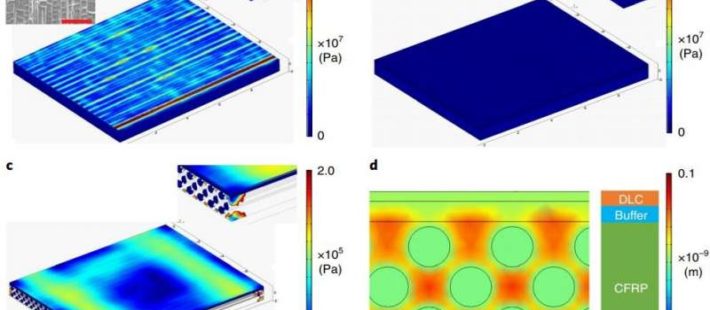
Surrey engineers have shown that their thin nano-barrier ‒ measuring only sub-micrometers in thickness, compared to the tens of micrometers of current space mission coatings ‒ is less susceptible to stress and contamination at the surface, keeping its integrity even after multiple thermal cycles.
Professor Ravi Silva, Director of the Advanced Technology Institute at the University of Surrey, said: “We are confident that the reinforced composite we have reported is a significant improvement over similar methods and materials already on the market. These encouraging results suggest that our barrier could eliminate the considerable costs and dangers associated with using carbon fibre reinforced polymers in space missions.”
Christian Wilhelmi, Head of Mechanical Subsystems and Research and Technology Friedrichshafen at Airbus Defence and Space, said: “We have been using carbon-fibre composites on our spacecraft and instrument structures for many years, but the newly developed nano-barrier together with our ultra-high-modulus CFRP manufacturing capability will enable us to create the next generation of non-outgassing CFRP materials with much more dimensional stability for optics and payload support. Reaching this milestone gives us the confidence to look at instrument-scale manufacturing to fully prove the technology.”
Professor David Sampson, Vice-Provost Research and Innovation at the University of Surrey, said: “This research project continues the University of Surrey’s long and close partnership with Airbus. Advanced materials for spacecraft is a further excellent example of how Surrey supports the Space Sector. We have been doing so for decades, and we are fully committed to strengthening our support for the sector going forwards. I look forward to more brilliant advances from the Surrey-Airbus relationship in years to come.”
Source : Phys.org
Photo : Stress modelling within CFRP and coated components. Credit: Nature Materials (2019).