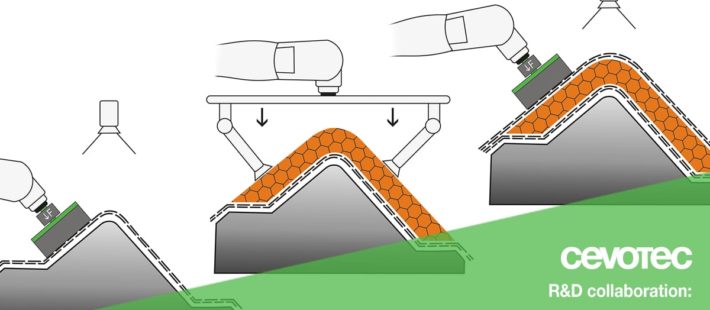
The continued effort to reduce emissions in the aerospace industry has led to the widespread adaptation of composite materials and sandwich structures. It is a major driver for new process developments and part certifications. Composite materials, in particular sandwich structures, offer very specific benefits. But as of today, they still greatly depend on manual labor and multiple, subsequent inspection steps to assure compliance with tight quality specifications.
By enhancing the automated Fiber Patch Placement (FPP) lay-up process with advanced on-line inspection capabilities, Cevotec strives to make the production of these components:
- more affordable
- more efficient
- and more controlled.
Cevotec CEO Thorsten Groene states
“The FPP technology is unique in its capability to lay-up fibers on surfaces with compound bends and we want to extend this to the automated lay-up of complete sandwich components, including the core materials”. Key targets of the project are to:
- increase the net lay-up speed by factor 7-10x to 15m²/h
- reduce the amount of manual labor needed by up to 100%
Cevotec’s scope of work encompasses both software and hardware developments. The first area of development is a further advancement of the patch placement process.
“We will implement an active force-feedback function on the robot integrated in our system to meet optimal compaction forces during the lay-up process while also enhancing our proprietary gripper technology”, explains Richard Carle, ACoSaLUS Project Lead at Cevotec.
Together with the Augsburg University of Applied Sciences
Cevotec works on optimization of their lay-up planning and simulation algorithms to reduce the overall cycle time per component and to further increase the quality of mechanical strength predictions. To ensure the produced components match the strict manufacturing specifications needed by aerospace customers and tier-one suppliers, Cevotec will develop a vision system to inspect the first and second skin laminates during the placement process.
This will be done in close cooperation with GKN Aerospace GmbH and VisCheck GmbH. New prepreg formulations developed by SGL Carbon will also be tested during the project to optimize their use on Cevotec systems. In addition, a gripper-based application technology for vacuum aids newly developed by Vabatec GmbH is to be elaborated.
At the end of the project in 2023, Cevotec aims to have improved the net lay-up speed of relevant components by factor 7-10x and to have developed a fully automated lay-up process for sandwich parts using Fiber Patch Placement technology, including advanced online inspection routines and self-adaptive process control, advanced placement routines, and automated core handling, with the objective to transfer the developments into aerospace series production.