The ability to arrange different types of fibres with predetermined spatial organisation gives us the colour, vibrancy and comfort we encounter in traditional textiles.
Replace conventional fibres with those that can conduct electricity and we introduce new dimensions. Researchers introduce the ability to monitor human movement using wearable garments, and even to store the energy required to power such a function.
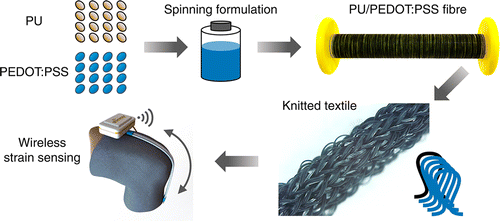
Centre of Excellence for Electromaterials Science (ACES) researchers have created new fibre structures and used traditional knitting and braiding techniques to introduce both of these capabilities to wearable structures (ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, “knitted Strain Sensor Textiles of Highly Conductive All-Polymeric Fibers”).
A knitted textile based on the polymeric composite fibres, produced at the Australian National Fabrication Facility, is highly sensitive, stable and able to detect a wide range of human movement.
The team demonstrated a working device with remote sensing capabilities using a knee sleeve prototype of the fabric that ‘talks’ to a commercial wireless receiver.
These fibres are not only stretchable but also conduct electricity. This combination of properties allows the fibres to respond to body movement. For energy storage, the materials that make up a battery have been braided into appropriate arrangements to deliver energy storage capabilities.
ACES researchers have created stretchable and electrically conductive fibres that can be braided and knitted using traditional techniques to create wearable garments that monitor human movement.